Crystal structure optimization
[Definition of energy]
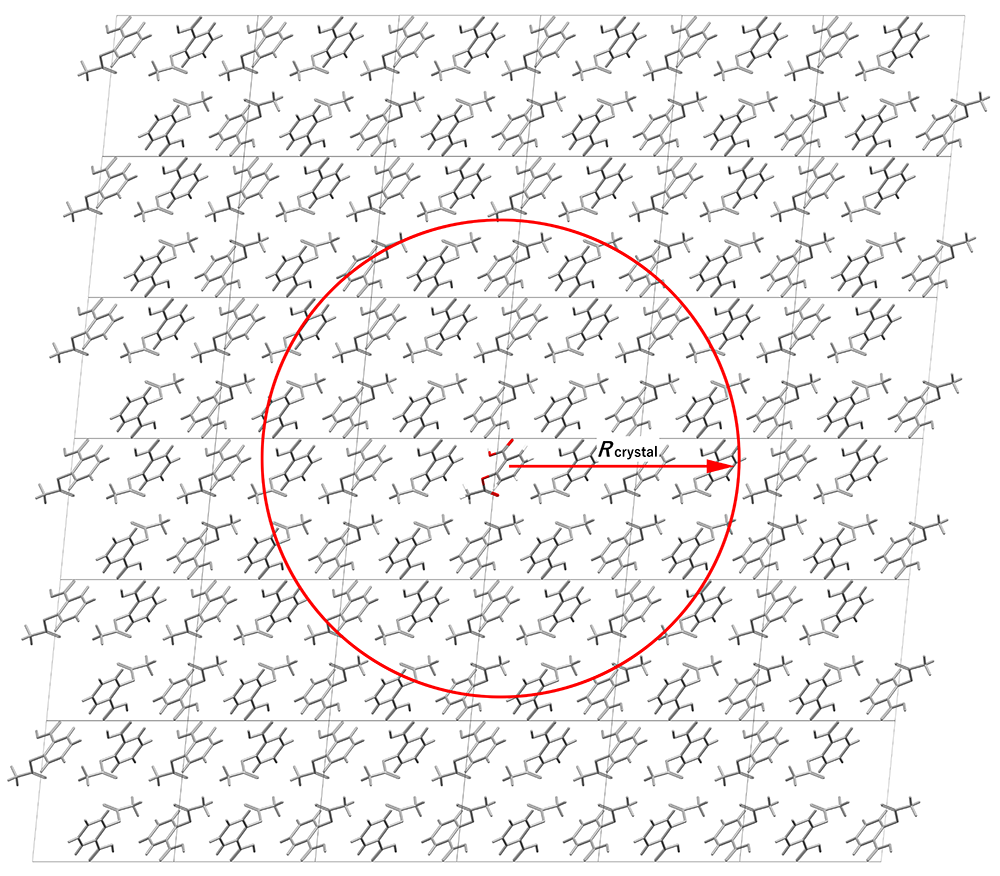
A crystal structure can be built by periodically arranging a unit cell through translational symmetry (Figure 1). The unit cell is defined by an asymmetric unit, lattice constants, and space group symmetry. Therefore, in simulations, the crystal structure is constructed using the asymmetric unit, the lattice constants, the space group symmetry, and the translational symmetry, and an energy of the crystal is defined by the equation 1 as the energy per asymmetric unit.
Here, the Eintra is the sum of intramolecular interaction energies in the asymmetric unit, and the Elattice is defined by the equation 2. In the equation 2, the EAUinter is the sum of intermolecular interaction energies in the asymmetric unit. When the number of molecules in the asymmetric unit is one, the the EAUinter is zero. The second term in the equation 2 is the sum of intermolecular interaction energies between the molecule(s) in the asymmetric unit and molecules replicated by symmetry operations within a cut-off radius Rcrystal in the real space. The Ewald method is applied to the calculation of electrostatic interactions.
The Ewald method calculates coulombic potential using four terms of real space term, Φreal, reciprocal space term, Φrecip, self energy term, Φself, surface term, Φsurf. By default, the Φsurf term is omitted. This term can be activated by a keyword. Please refer to the manual.
Here, the q is atomic charge, the α is Ewald convergence parameter, the |ri;S,J| is interatomic distance, the V is volume of the unit cell, the n′ is reciprocal lattice vector, and the r is position vector of atom in the unit cell. The Z is the number of the smallest building blocks (the asymmetric unit and replicated units created by applying symmetry operations to the asymmetric unit) in the unit cell. The parameter α and the cutoff distance in the reciprocal lattice space are automatically determined so that the interatomic interaction energy is smaller than 10-8 based on the cutoff distance in the real space. The values of these parameters can be specified by keywords. Please refer to the manual.
[Types of crystal structure optimization]
The program can perform three types of crystal structure optimization, as shown blow. These optimizations are performed under a specified space group symmetry.
- Molecular geometry optimization in a crystal environment (MOL)
- The geometry, orientation, and position of the molecules in the crystal are optimized, while the lattice constants remain fixed during the calculation.
- Crystal structure optimization assuming rigid molecules (RIGID)
- The orientation and position of the molecules, as well as the lattice constants, are optimized, while the molecular geometry remains fixed during the calculation.
- Full optimization of crystal structure (ALL)
- All degrees of freedom that define the crystal structure, that is, the molecular geometry, orientation, and position as well as the lattice constants are relaxed.
[Execution of crystal structure optimization]
This section explains how to perform crystal structure optimization. To execute this, the following input data is required: atomic coordinates of the asymmetric unit, lattice constants, and space group. For this example, we use a crystal of hydroxy malonic acid, which is a derivative of malonic acid (Roelofsen, G.; Kanters, J.A.; Kroon, J.; Doesburg, H.M.; Koops, T. Acta Cryst.1978, B34, 2565.).
In the case of using CMF file
We prepare the tartronicacid.cmf file, shown below, as input file. The tartronicacid.cmf contains the crystal structure data of hydroxy malonic acid in CIFMIF format (Combined CIF and MIF file, where CIF stands for Crystallographic Information File and MIF stands for Molecular Information File). You can find the tartronicacid.cmf file in the Sample_Files folder, located in the CONFLEX installation directory (Sample_Files\CONFLEX\crystal\optimization\cmf_file\tartronicacid.cmf).
tartronicacid.cmf file
data_Tartronicacid _symmetry_cell_setting ORTHORHOMBIC _symmetry_space_group_name_H-M 'P212121 ' _ccdc_symmetry_space_group_name P212121 _symmetry_Int_Tables_number 19 loop_ _symmetry_equiv_pos_site_id _symmetry_equiv_pos_as_xyz 1 x,y,z 2 1/2+x,1/2-y,-z 3 -x,1/2+y,1/2-z 4 1/2-x,-y,1/2+z _cell_length_a 4.49400 _cell_length_b 8.81900 _cell_length_c 10.88200 _cell_angle_alpha 90.00000 _cell_angle_beta 90.00000 _cell_angle_gamma 90.00000 _cell_formula_units_Z 4 _cell_volume 431.28180 _exptl_crystal_density_diffrn 1.84821 loop_ _ccdc_atom_site_atom_id_number _atom_site_label _atom_site_type_symbol _atom_site_fract_x _atom_site_fract_y _atom_site_fract_z _ccdc_atom_site_symmetry _ccdc_atom_site_base 1 O1 O 1.12990 -0.13910 0.36040 1_555 1 2 O2 O 0.97510 0.09280 0.30700 1_555 2 3 O3 O 1.01480 0.11550 0.66290 1_555 3 4 O4 O 1.13030 -0.12820 0.62810 1_555 4 5 O5 O 0.57240 0.09790 0.48970 1_555 5 6 C1 C 0.97750 -0.01540 0.37600 1_555 6 7 C2 C 0.78810 -0.01520 0.49230 1_555 7 8 C3 C 0.99010 -0.00160 0.60420 1_555 8 9 H1 H 0.66800 -0.11200 0.49600 1_555 9 10 H2 H 0.60500 0.14900 0.45600 1_555 10 11 H3 H 1.23700 -0.13800 0.31000 1_555 11 12 H4 H 1.27100 -0.12000 0.68000 1_555 12 loop_ _atom_id _atom_type _atom_attach_nh _atom_attach_h _atom_charge 1 O 1 1 0 2 O 1 0 0 3 O 1 0 0 4 O 1 1 0 5 O 1 1 0 6 C 3 0 0 7 C 3 1 0 8 C 3 0 0 loop_ _bond_id_1 _bond_id_2 _bond_type_ccdc _bond_environment 1 6 S chain 1 11 S chain 2 6 D chain 3 8 D chain 4 8 S chain 4 12 S chain 5 7 S chain 5 10 S chain 6 7 S chain 7 8 S chain 7 9 S chain
[Execution from Interface]
Open the tartronicacid.cmf file using CONFLEX Interface.
Select [CONFLEX] from the Calculation menu, and then click in the calculation setting dialog that appears.
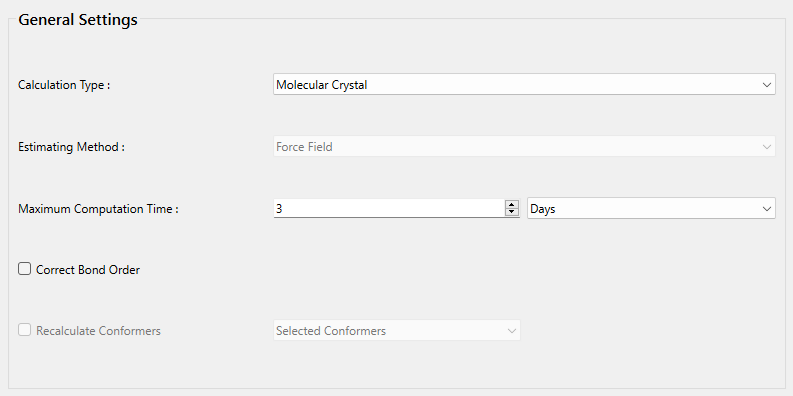
Next, in [General Settings] dialog of the detailed settings dialog, select [Molecular Crystal] from the pull-down menu of [Calculation Type:].
The settings for the crystal calculation are configured in the [Crystal Calculation] dialog.
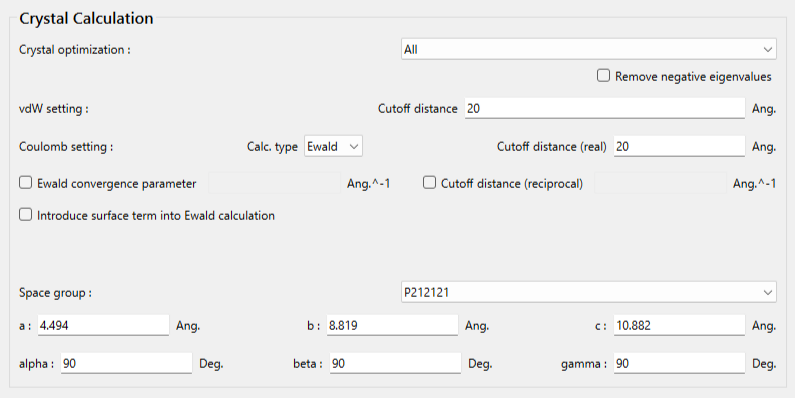
The type of crystal structure optimization can be changed using the pull-down menu of [Crystal Optimization:]. The default setting is "ALL". In this dialog, you can also change settings for calculating intermolecular interactions such as the cutoff distance and the method for calculating Coulombic interactions, and other related parameters.
After completing the calculation settings, click to start the calculation.
[Execution from command line]
The calculation settings are defined by specifying keywords in the tartronicacid.ini file.
tartronicacid.ini file
CRYSTAL MMFF94S
[CRYSTAL] indicates that a crystal calculation will be performed. By default, CONFLEX carries out a full optimization of crystal structure (ALL). If you want to change the type of crystal structure optimization, use the [CRYSTAL_OPTIMIZATION=] keyword. For example: [CRYSTAL_OPTIMIZATION=MOL].
[MMFF94s] means to use MMFF94s force field.
Store the two files of tartronicacid.cmf and tartronicacid.ini in a single folder, and execute the following command to start the calculation.
C:\CONFLEX\bin\conflex-10a.exe -par C:\CONFLEX\par tartronicacidenter
The command above is for Windows OS. For other OS, please refer to [How to execute CONFLEX].
In the case of using CIF file
In a CIF file, bond information (such as bond orders) is not included, although atomic coordinates of the molecule in the asymmetric unit, lattice constants, and space group information are provided.
Therefore, to perform a crystal calculation, you have to specify the bonding between atoms using the "CIF_BOND=" keyword.
When a calculation is executed via the CONFLEX Interface, the program automatically generates the bond information.
In this section, we use tartronicacid.cif file, which contains the crystal structure data of hydroxy malonic acid in CIF format.
This file is located in Sample_Files folder in the CONFLEX installation directory (Sample_Files\CONFLEX\crystal\optimization\cif_file\tartronicacid.cif)
tartronicacid.cif file
data_Tartronicacid _symmetry_cell_setting ORTHORHOMBIC _symmetry_space_group_name_H-M 'P212121 ' _symmetry_Int_Tables_number 19 loop_ _symmetry_equiv_pos_as_xyz x,y,z -x+1/2,-y,z+1/2 -x,y+1/2,-z+1/2 x+1/2,-y+1/2,-z _cell_length_a 4.49400 _cell_length_b 8.81900 _cell_length_c 10.88200 _cell_angle_alpha 90.00000 _cell_angle_beta 90.00000 _cell_angle_gamma 90.00000 _cell_formula_units_Z 4 _cell_volume 431.28180 loop_ _atom_site_label _atom_site_type_symbol _atom_site_fract_x _atom_site_fract_y _atom_site_fract_z O1 O 1.12990 -0.13910 0.36040 O2 O 0.97510 0.09280 0.30700 O3 O 1.01480 0.11550 0.66290 O4 O 1.13030 -0.12820 0.62810 O5 O 0.57240 0.09790 0.48970 C1 C 0.97750 -0.01540 0.37600 C2 C 0.78810 -0.01520 0.49230 C3 C 0.99010 -0.00160 0.60420 H1 H 0.66800 -0.11200 0.49600 H2 H 0.60500 0.14900 0.45600 H3 H 1.23700 -0.13800 0.31000 H4 H 1.27100 -0.12000 0.68000
[Execution from Interface]
Open tartronicacid.cif file using CONFLEX Interface
Select [CONFLEX] from the Calculation menu, and then click in the calculation setting dialog that appears.
Next, in [General Settings] dialog of the detailed settings dialog, select [Molecular Crystal] from the pull-down menu of [Calculation Type:] and check the check box of [Correct Bond Order] to correct bond order.
The settings for the crystal calculation are configured in the [Crystal Calculation] dialog.

The type of crystal structure optimization can be changed using the pull-down menu of [Crystal Optimization:].
The default setting is "ALL". In this dialog, you can also change settings for calculating intermolecular interactions such as the cutoff distance and the method for calculating Coulombic interactions, and other related parameters.
When completing the calculation settings, click to start the calculation.
[Execution from command line]
The calculation settings are defined by specifying keywords in the tartronicacid.ini file.
tartronicacid.ini file
CRYSTAL MMFF94S CIF_BOND=(1,6,1) CIF_BOND=(1,11,1) CIF_BOND=(2,6,2) CIF_BOND=(3,8,2) CIF_BOND=(4,8,1) CIF_BOND=(4,12,1) CIF_BOND=(5,7,1) CIF_BOND=(5,10,1) CIF_BOND=(6,7,1) CIF_BOND=(7,8,1) CIF_BOND=(7,9,1)
[CRYSTAL] indicates that a crystal calculation will be performed. By default, CONFLEX carries out a full optimization of crystal structure (ALL). If you want to change the type of crystal structure optimization, use the [CRYSTAL_OPTIMIZATION=] keyword. For example: [CRYSTAL_OPTIMIZATION=MOL].
[MMFF94s] means to use MMFF94s force field.
[CIF_BOND=] is used to define the bond information for the hydroxy malonic acid molecule.
To specify a bond with bond order n between atoms i and j, use the keyword in the following format: CIF_BOND=(i,j,n)
Store the two files of tartronicacid.cif and tartronicacid.ini in a single folder, and execute the following command to start the calculation.
C:\CONFLEX\bin\conflex-10a.exe -par C:\CONFLEX\par tartronicacidenter
The command above is for Windows OS. For other OS, please refer to [How to execute CONFLEX].
In the case of using MOL file
The molecule in the MDL-MOL file is used as the asymmetric unit. Therefore, when using a MDL-MOL file for crystal calculations, you should pay attention to the orientation and spatial position of the molecule. Depending on these factors, symmetry operations may cause steric clashes between molecules in the crystal. Here, we prepare the tartronicacid.mol file, shown below, as input file. The tartronicacid.mol contains the structure data of hydroxy malonic acid molecule in MDL-MOL format. This file is located in Sample_Files folder in the CONFLEX installation directory (Sample_Files\CONFLEX\crystal\optimization\mol_file\tartronicacid.mol).
tartronicacid.mol file
Tartronicacid.mol
12 11 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 V2000
5.0778 -1.2267 3.9219 O 0 0 0 0 0
4.3821 0.8184 3.3408 O 0 0 0 0 0
4.5605 1.0186 7.2137 O 0 0 0 0 0
5.0796 -1.1306 6.8350 O 0 0 0 0 0
2.5724 0.8634 5.3289 O 0 0 0 0 0
4.3929 -0.1358 4.0916 C 0 0 0 0 0
3.5417 -0.1340 5.3572 C 0 0 0 0 0
4.4495 -0.0141 6.5749 C 0 0 0 0 0
3.0020 -0.9877 5.3975 H 0 0 0 0 0
2.7189 1.3140 4.9622 H 0 0 0 0 0
5.5591 -1.2170 3.3734 H 0 0 0 0 0
5.7119 -1.0583 7.3998 H 0 0 0 0 0
1 6 1 0 0
1 11 1 0 0
2 6 2 0 0
3 8 2 0 0
4 8 1 0 0
4 12 1 0 0
5 7 1 0 0
5 10 1 0 0
6 7 1 0 0
7 8 1 0 0
7 9 1 0 0
M END
[Execution from Interface]
Open the tartronicacid.mol file using CONFLEX Interface.
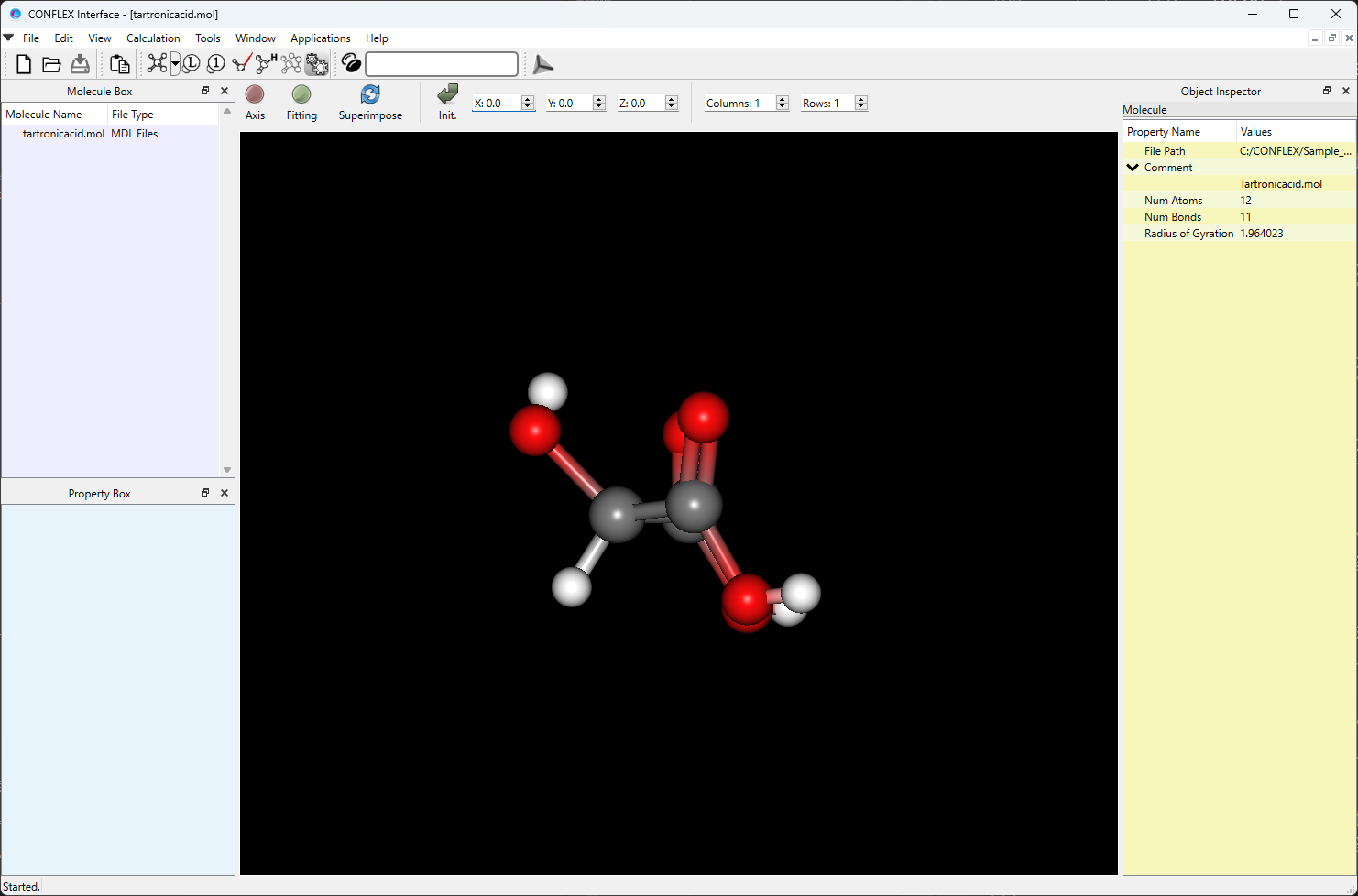
Select [CONFLEX] from the Calculation menu, click in the calculation setting dialog that appears.
Next, in [General Settings] dialog of the detailed settings dialog, select [Molecular Crystal] from the pull-down menu of [Calculation Type:].

The settings for the crystal calculation are configured in the [Crystal Calculation] dialog.
The type of crystal structure optimization can be changed using the pull-down menu of [Crystal Optimization:].
The default setting is "ALL". In this dialog, you can also change settings for calculating intermolecular interactions such as the cutoff distance and the method for calculating Coulombic interactions, and other related parameters.
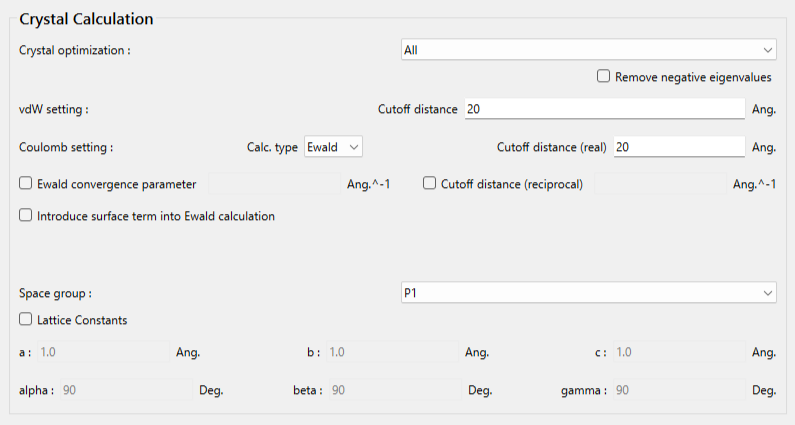
The tartronicacid.mol file does not include space group and lattice constant information. Therefore, these parameters need to be set manually in this dialog.
To set the space group, select P212121 from the [Space group:] pull-down menu.
Next, to enter the lattice constants, check the [Lattice Constants] checkbox, and input the values accordingly.
The lattice constants for the crystal structure of hydroxy malonic acid are a=4.494 Å,b=8.819 Å,c=10.882 Å,α=90.0 °,β=90.0 °,γ=90.0 °.
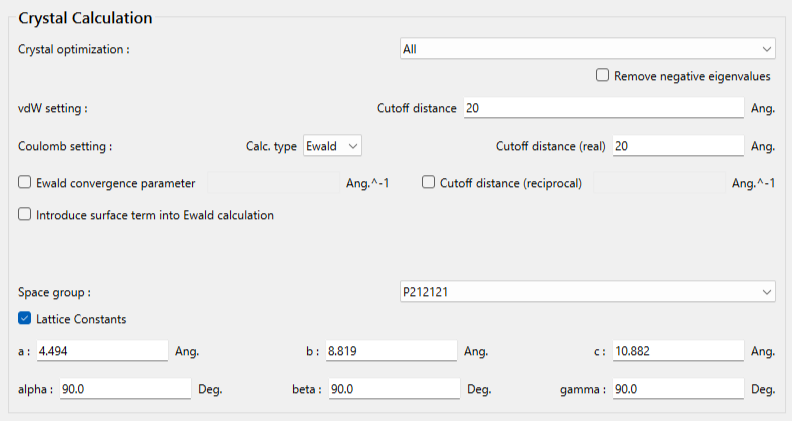
After completing the calculation settings, click to start the calculation.
[Execution from command line]
The calculation settings are defined by specifying keywords in the tartronicacid.ini file.
tartronicacid.ini file
CRYSTAL MMFF94S SPACE_GROUP=P212121 LATTICE_CONSTANT=(4.494,8.819,10.882,90.0,90.0,90.0)
[CRYSTAL] indicates that a crystal calculation will be performed. By default, CONFLEX carries out a full optimization of crystal structure (ALL). If you want to change the type of crystal structure optimization, use the [CRYSTAL_OPTIMIZATION=] keyword. For example: [CRYSTAL_OPTIMIZATION=MOL].
[MMFF94s] means to use MMFF94s force field.
The tartronicacid.mol file does not include space group and lattice constant information.
These parameters should be specified using the [SPACE_GROUP=] and [LATTICE_CONSTANT=] keywords.
For the crystal structure of hydroxy malonic acid, the space group is P212121, and the lattice constants are: a=4.494 Å,b=8.819 Å,c=10.882 Å,α=90.0 °,β=90.0 °,γ=90.0 °.
Store the two files of tartronicacid.mol and tartronicacid.ini in a single folder, and execute the following command to start the calculation.
C:\CONFLEX\bin\conflex-10a.exe -par C:\CONFLEX\par tartronicacidenter
The command above is for Windows OS. For other OS, please refer to [How to execute CONFLEX].
[Structure optimization with constrains]
When there is more than one molecule in the asymmetric unit, CONFLEX can perform crystal structure optimization with constraints using one of the two methods described below. These methods are cannot be used simultaneously.
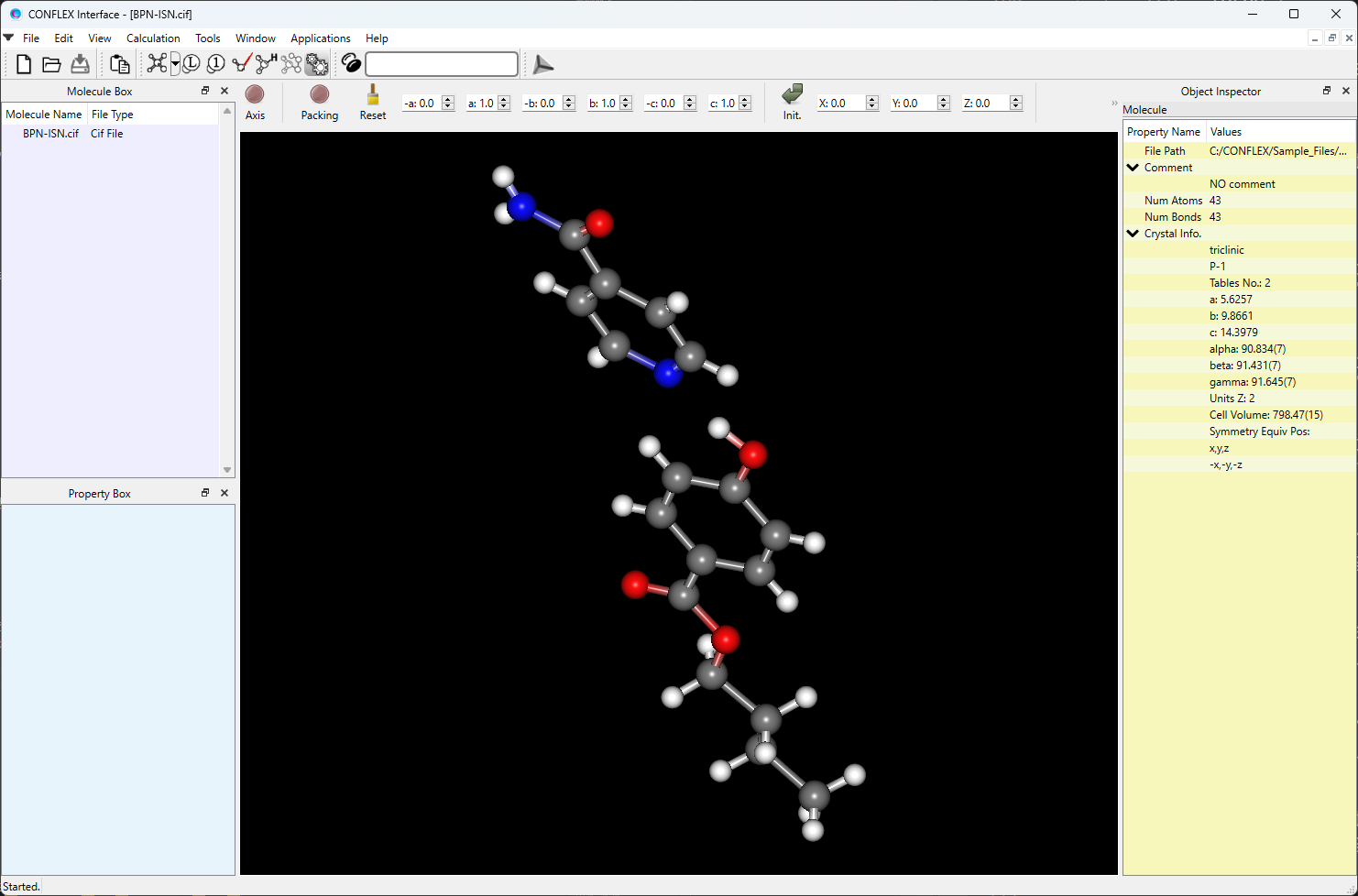
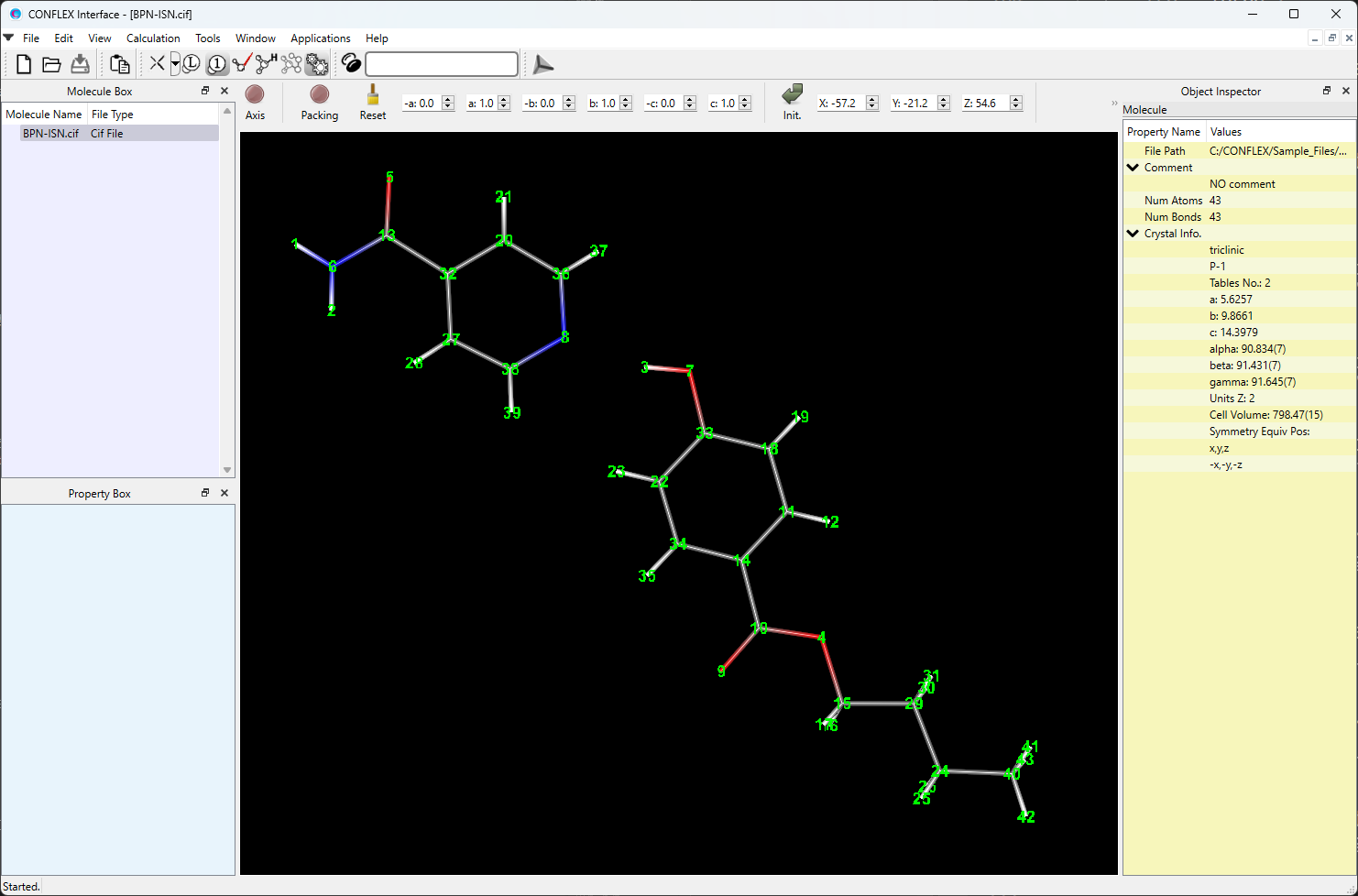
Here, to explain these functions, we use the co-crystal butylparaben–isonicotinamide. From the supporting information of Bhardwaj’s paper [R. M. Bhardwaj, H. Yang and A. J. Florence, Acta Cryst. (2016). E72, 53-55], the structure of this co-crystal is available as cv5494sup1.cif. The cv5494sup1.cif is modified for treating by CONFLEX program and the modified version is saved as BPN-ISN.cif. The BPN-ISN.cif file is located in Sample_Files folder in the CONFLEX installation directory (Sample_Files\CONFLEX\crystal\molecular.fixing\BPN-ISN.cif).
BPN-ISN.cif file
data_I _symmetry_cell_setting triclinic _symmetry_Int_Tables_number 2 _symmetry_space_group_name_H-M 'P-1' loop_ _symmetry_equiv_pos_as_xyz x,y,z -x,-y,-z _cell_length_a 5.6257(6) _cell_length_b 9.8661(11) _cell_length_c 14.3979(15) _cell_angle_alpha 90.834(7) _cell_angle_beta 91.431(7) _cell_angle_gamma 91.645(7) _cell_volume 798.47(15) _cell_formula_units_Z 2 loop_ _atom_site_type_symbol _atom_site_label _atom_site_fract_x _atom_site_fract_y _atom_site_fract_z _atom_site_U_iso_or_equiv _atom_site_adp_type _atom_site_calc_flag _atom_site_occupancy _atom_site_disorder_assembly _atom_site_disorder_group H H1N -0.623(3) 1.480(2) 1.4226(13) 0.019(5) Uiso d 1 . . H H2N -0.626(4) 1.399(2) 1.3256(16) 0.035(6) Uiso d 1 . . H H3O 0.140(5) 0.939(3) 1.1807(17) 0.054(7) Uiso d 1 . . O O4 0.1197(2) 0.47988(13) 0.82145(8) 0.0227(3) Uani d 1 . . O O1 -0.2641(2) 1.38157(14) 1.49057(9) 0.0275(3) Uani d 1 . . N N1 -0.5594(3) 1.41555(17) 1.38514(11) 0.0238(4) Uani d 1 . . O O2 0.2637(2) 0.88155(15) 1.16227(9) 0.0308(4) Uani d 1 . . N N2 -0.0392(3) 1.05682(16) 1.24155(10) 0.0234(4) Uani d 1 . . O O3 -0.2134(2) 0.59634(14) 0.80166(9) 0.0297(3) Uani d 1 . . C C13 -0.0315(3) 0.57543(19) 0.84578(12) 0.0207(4) Uani d 1 . . C C7 0.2633(3) 0.63083(19) 0.97609(12) 0.0220(4) Uani d 1 . . H H8 0.3619 0.5641 0.9542 0.026 Uiso calc 1 . . C C6 -0.3631(3) 1.35566(18) 1.41440(12) 0.0194(4) Uani d 1 . . C C12 0.0462(3) 0.65243(18) 0.93023(12) 0.0190(4) Uani d 1 . . C C14 0.0586(3) 0.40447(19) 0.73615(12) 0.0223(4) Uani d 1 . . H H15A 0.0438 0.4660 0.6845 0.027 Uiso calc 1 . . H H15B -0.0918 0.3552 0.7423 0.027 Uiso calc 1 . . C C8 0.3330(3) 0.7076(2) 1.05364(13) 0.0239(4) Uani d 1 . . H H9 0.4775 0.6920 1.0839 0.029 Uiso calc 1 . . C C2 -0.0520(3) 1.18936(19) 1.38204(13) 0.0234(4) Uani d 1 . . H H2 0.0162 1.2121 1.4399 0.028 Uiso calc 1 . . C C10 -0.0302(3) 0.83018(19) 1.04128(12) 0.0229(4) Uani d 1 . . H H11 -0.1290 0.8969 1.0631 0.027 Uiso calc 1 . . C C16 0.2264(3) 0.2420(2) 0.62252(13) 0.0242(4) Uani d 1 . . H H17A 0.0722 0.1955 0.6171 0.029 Uiso calc 1 . . H H17B 0.2306 0.3126 0.5764 0.029 Uiso calc 1 . . C C5 -0.3533(3) 1.21153(19) 1.26476(12) 0.0213(4) Uani d 1 . . H H6 -0.4918 1.2498 1.2420 0.026 Uiso calc 1 . . C C15 0.2548(3) 0.30708(19) 0.71924(12) 0.0220(4) Uani d 1 . . H H16A 0.2511 0.2370 0.7658 0.026 Uiso calc 1 . . H H16B 0.4075 0.3551 0.7248 0.026 Uiso calc 1 . . C C1 -0.2580(3) 1.25031(18) 1.35125(12) 0.0185(4) Uani d 1 . . C C9 0.1866(3) 0.80852(19) 1.08652(12) 0.0221(4) Uani d 1 . . C C11 -0.0986(3) 0.75279(19) 0.96404(12) 0.0223(4) Uani d 1 . . H H12 -0.2437 0.7680 0.9342 0.027 Uiso calc 1 . . C C3 0.0504(3) 1.0945(2) 1.32551(13) 0.0251(4) Uani d 1 . . H H3 0.1888 1.0544 1.3467 0.030 Uiso calc 1 . . C C4 -0.2387(3) 1.11486(19) 1.21283(13) 0.0240(4) Uani d 1 . . H H5 -0.3042 1.0892 1.1551 0.029 Uiso calc 1 . . C C17 0.4194(4) 0.1414(2) 0.60224(14) 0.0314(5) Uani d 1 . . H H18A 0.5725 0.1869 0.6068 0.047 Uiso calc 1 . . H H18B 0.3946 0.1042 0.5407 0.047 Uiso calc 1 . . H H18C 0.4130 0.0696 0.6465 0.047 Uiso calc 1 . .
* Constraint by harmonic potential
In structure optimization, restrictions on structural changes can be imposed on interatomic distances, bond angles, dihedral angles, and out-of-plane angles defined between molecules in the asymmetric unit using harmonic potentials. These harmonic potentials are specified using the keywords described below.
| Structural parameter | Keyword | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Interatomic distance | CRYSTAL_PSEUDO_DIST=(I,J,STD,FK) | The harmonic potential with the standard distance STD (Å) and the force constant FK (kcal・mol-1・Å-2) is applied to the interatomic distance between atoms I and J. |
| Angle | CRYSTAL_PSEUDO_ANGL=(I,J,K,STD,FK) | The harmonic potential with the standard angle STD (°) and the force constant FK (kcal・mol-1・rad-2) is applied to the angle of I-J-K. |
| Dihedral angle | CRYSTAL_PSEUDO_TORS=(I,J,K,L,STD,FK) | The harmonic potential with the standard angle STD (°) and the force constant FK (kcal・mol-1・rad-2) is applied to the dihedral angle of I-J-K-L. |
| Out of plane angle | CRYSTAL_PSEUDO_OOPL=(I,J,K,L,STD,FK) | The harmonic potential with the standard angle STD (°) and the force constant FK (kcal・mol-1・rad-2) is applied to the out of plane angle of I=J-K(-L). |
[Execution from Interface]
Open the BPN-ISN.cif file using CONFLEX Interface.
Select [CONFLEX] from the Calculation menu, and then click in the calculation setting dialog that appears.
Next, in [General Settings] dialog of the detailed settings dialog, select [Molecular Crystal] from the pull-down menu of [Calculation Type:] and check the check box of [Correct Bond Order] to correct bond order.

The settings for the crystal calculation are configured in the [Crystal Calculation] dialog.
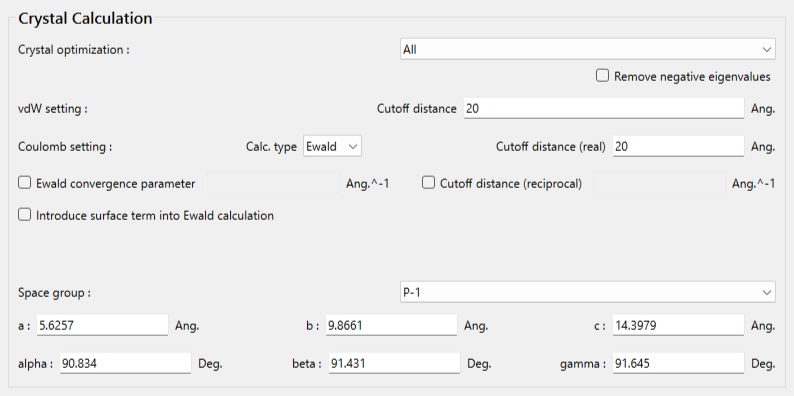
Select [All] from the pull-down menu of [Crystal optimization:] on this dialog. Other optimization methods are also available. Next, click in the detailed settings dialog.
A dialog displaying the keywords for the calculation settings will appear.
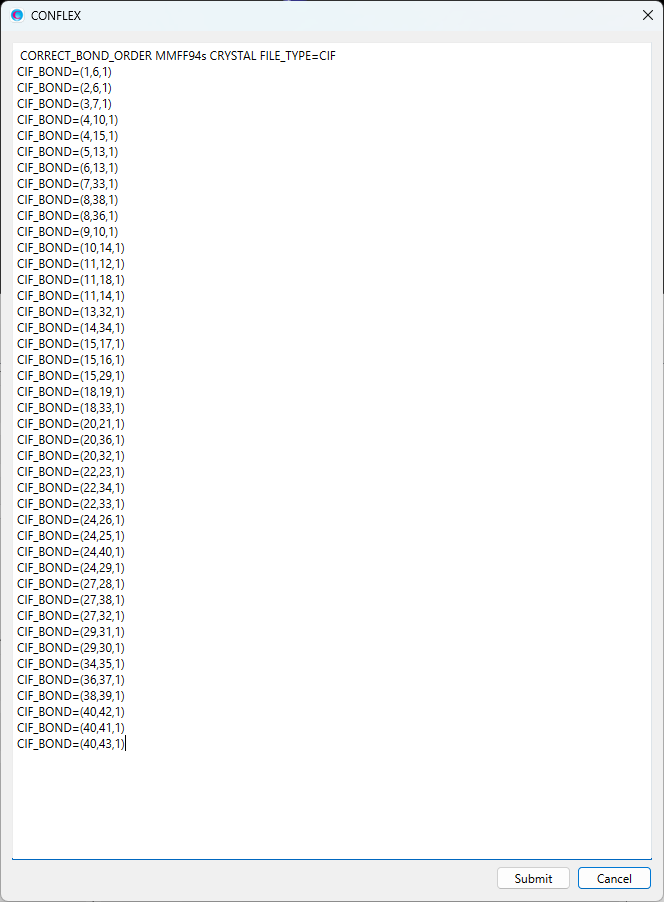
Here, we apply harmonic potentials to the interatomic distance between hydrogen (I=3) and nitrogen (J=8) atoms, and to the angle defined by hydrogen (I=3), oxygen (J=7), and nitrogen (K=8) atoms. To do this, two new keywords need to be added to the dialog.
CRYSTAL_PSEUDO_DIST=(3,8,1.794,10000.0) CRYSTAL_PSEUDO_ANGL=(3,7,8,10.15,10000.0)
The modified dialog is shown below.
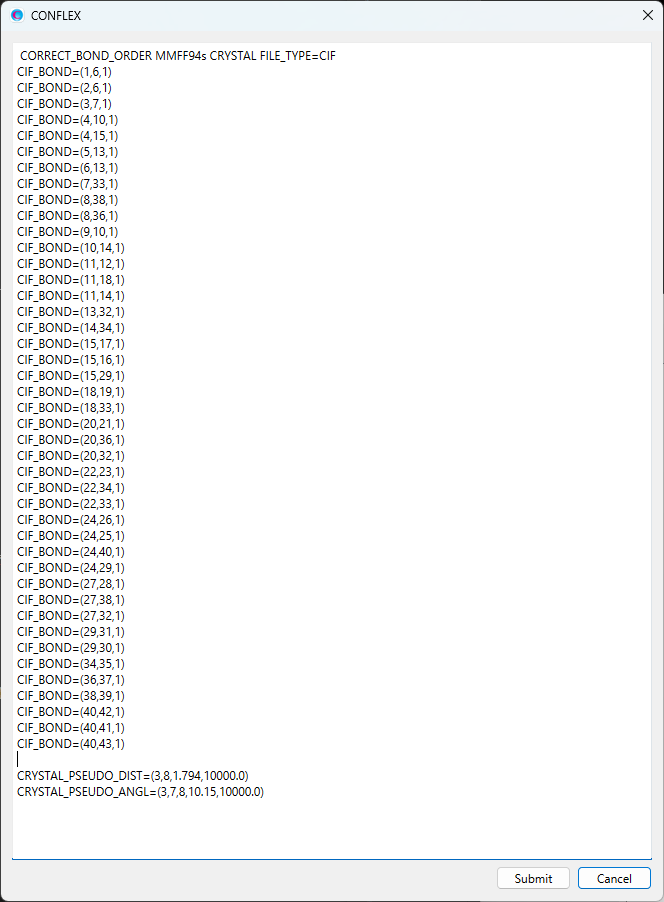
When completing the modifications, click to start the calculation. In the optimized structure, each structural parameter constrained by the harmonic potentials is approximately equal to the standard value STD.
[Execution from command line]
The calculation settings are defined by specifying keywords in the BPN-ISN.ini file.
BPN-ISN.ini file
CRYSTAL MMFF94S CRYSTAL_PSEUDO_DIST=(3,8,1.794,10000.0) CRYSTAL_PSEUDO_ANGL=(3,7,8,10.15,10000.0) CIF_BOND=(1,6,1) CIF_BOND=(2,6,1) CIF_BOND=(3,7,1) CIF_BOND=(4,10,1) CIF_BOND=(4,15,1) CIF_BOND=(5,13,2) CIF_BOND=(6,13,1) CIF_BOND=(7,33,1) CIF_BOND=(8,38,2) CIF_BOND=(8,36,1) CIF_BOND=(9,10,2) CIF_BOND=(10,14,1) CIF_BOND=(11,12,1) CIF_BOND=(11,18,1) CIF_BOND=(11,14,2) CIF_BOND=(13,32,1) CIF_BOND=(14,34,1) CIF_BOND=(15,17,1) CIF_BOND=(15,16,1) CIF_BOND=(15,29,1) CIF_BOND=(18,19,1) CIF_BOND=(18,33,2) CIF_BOND=(20,21,1) CIF_BOND=(20,36,2) CIF_BOND=(20,32,1) CIF_BOND=(22,23,1) CIF_BOND=(22,34,2) CIF_BOND=(22,33,1) CIF_BOND=(24,26,1) CIF_BOND=(24,25,1) CIF_BOND=(24,40,1) CIF_BOND=(24,29,1) CIF_BOND=(27,28,1) CIF_BOND=(27,38,1) CIF_BOND=(27,32,2) CIF_BOND=(29,31,1) CIF_BOND=(29,30,1) CIF_BOND=(34,35,1) CIF_BOND=(36,37,1) CIF_BOND=(38,39,1) CIF_BOND=(40,42,1) CIF_BOND=(40,41,1) CIF_BOND=(40,43,1)
Here, we apply harmonic potentials to the interatomic distance between hydrogen (I=3) and nitrogen (J=8) atoms, and to the angle defined by hydrogen (I=3), oxygen (J=7), and nitrogen (K=8) atoms, using PSEUDO_***= keywords.
[CRYSTAL] indicates that a crystal calculation will be performed.
[MMFF94s] means to use MMFF94s force field.
[CIF_BOND=] is used to define the bond information for the isonicotinamide and butylparaben molecules.
To specify a bond with bond order n between atoms i and j, use the keyword in the following format: CIF_BOND=(i,j,n).
Store the two files of BPN-ISN.cif and BPN-ISN.ini in a single folder, and execute the following command to start the calculation. In the optimized structure, each structural parameter constrained by the harmonic potentials is approximately equal to the standard value STD.
C:\CONFLEX\bin\conflex-10a.exe -par C:\CONFLEX\par BPN-ISNenter
The command above is for Windows OS. For other OS, please refer to [How to execute CONFLEX].
* Constraints of structure and position of specified molecule
The following operations allow for crystal structure optimization while fixing the structure and position of a specified molecule.
[Execution from Interface]
Open the BPN-ISN.cif file using CONFLEX Interface.

Select [CONFLEX] from the Calculation menu, and then click in the calculation setting dialog that appears.
Next, in [General Settings] dialog of the detailed settings dialog, select [Molecular Crystal] from the pull-down menu of [Calculation Type:] and check the check box of [Correct Bond Order] to correct bond order.

The settings for the crystal calculation are configured in the [Crystal Calculation] dialog.
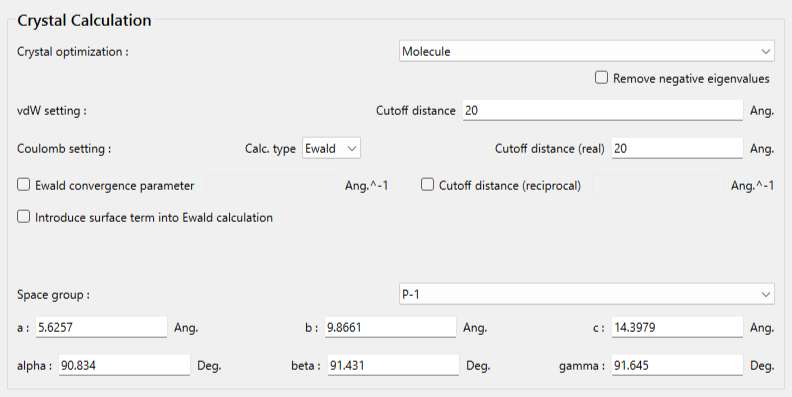
Select [Molecule] from the pull-down menu of [Crystal optimization:] on this dialog. Other methods cannot be used.
Next, click in the detailed settings dialog.
A dialog displaying the keywords for the calculation settings will appear.
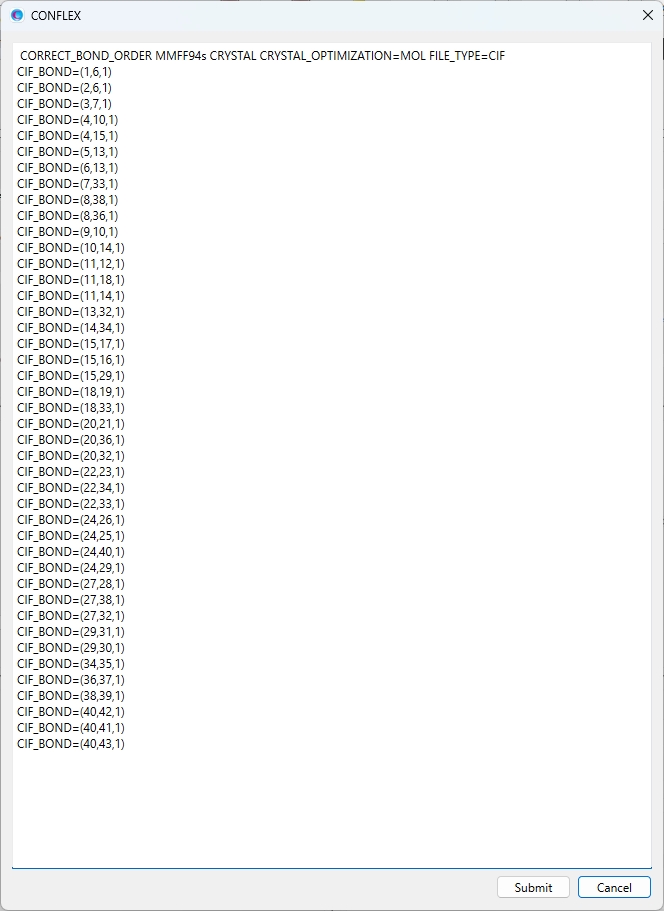
The molecule to be frozen during crystal structure optimization is defined by the [CRYSTAL_FIXED_MOL=] keyword.
The molecular ID of each molecule in the input file is automatically determined based on the atom serial number.
For example, in the case of BPN-ISN.cif, the molecular ID for isonicotinamide is 1 and it for butylparaben is 2.
To freeze the structure and position of butylparaben, we add the [CRYSTAL_FIXED_MOL=2] keyword to this dialog.
If you want to optimize the hydrogen atom positions of butylparaben, you should also add the [CRYSTAL_FIXED_MOL=EXCLUDE_HYDROGEN] keyword to this dialog.
The modified dialog is shown below.
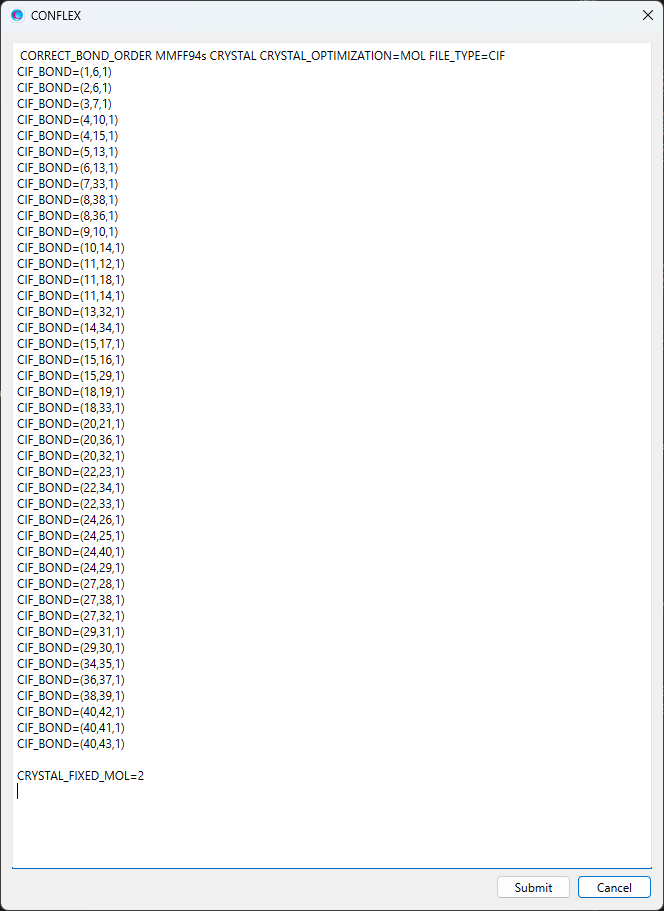
When completing the modifications, click to start the calculation. The structure and position of buthlparaben in the crystal are equivalent after and before the optimization.
[Execution from command line]
The calculation settings are defined by specifying keywords in the BPN-ISN.ini file.
BPN-ISN.ini file
CRYSTAL MMFF94S CRYSTAL_OPTIMIZATION=MOL CRYSTAL_FIXED_MOL=2 CIF_BOND=(1,6,1) CIF_BOND=(2,6,1) CIF_BOND=(3,7,1) CIF_BOND=(4,10,1) CIF_BOND=(4,15,1) CIF_BOND=(5,13,2) CIF_BOND=(6,13,1) CIF_BOND=(7,33,1) CIF_BOND=(8,38,2) CIF_BOND=(8,36,1) CIF_BOND=(9,10,2) CIF_BOND=(10,14,1) CIF_BOND=(11,12,1) CIF_BOND=(11,18,1) CIF_BOND=(11,14,2) CIF_BOND=(13,32,1) CIF_BOND=(14,34,1) CIF_BOND=(15,17,1) CIF_BOND=(15,16,1) CIF_BOND=(15,29,1) CIF_BOND=(18,19,1) CIF_BOND=(18,33,2) CIF_BOND=(20,21,1) CIF_BOND=(20,36,2) CIF_BOND=(20,32,1) CIF_BOND=(22,23,1) CIF_BOND=(22,34,2) CIF_BOND=(22,33,1) CIF_BOND=(24,26,1) CIF_BOND=(24,25,1) CIF_BOND=(24,40,1) CIF_BOND=(24,29,1) CIF_BOND=(27,28,1) CIF_BOND=(27,38,1) CIF_BOND=(27,32,2) CIF_BOND=(29,31,1) CIF_BOND=(29,30,1) CIF_BOND=(34,35,1) CIF_BOND=(36,37,1) CIF_BOND=(38,39,1) CIF_BOND=(40,42,1) CIF_BOND=(40,41,1) CIF_BOND=(40,43,1)
The molecule to be frozen during crystal structure optimization is defined by the [CRYSTAL_FIXED_MOL=] keyword. The molecular ID of each molecule in the input file is automatically determined based on the atom serial number. For example, in the case of BPN-ISN.cif, the molecular ID for isonicotinamide is 1 and it for butylparaben is 2. To freeze the structure and position of butylparaben, we add the [CRYSTAL_FIXED_MOL=2] keyword to the ini file. If you want to optimize the hydrogen atom positions of butylparaben, you should also add the [CRYSTAL_FIXED_MOL=EXCLUDE_HYDROGEN] keyword to the ini file.
In the case of optimization with this restrictions, only the crystal structure optimization option [CRYSTAL_OPTIMIZATION=MOL] can be selected.
[CRYSTAL] indicates that a crystal calculation will be performed.
[MMFF94s] means to use MMFF94s force field.
[CIF_BOND=] is used to define the bond information for the isonicotinamide and butylparaben molecules.
To specify a bond with bond order n between atoms i and j, use the keyword in the following format: CIF_BOND=(i,j,n).

Store the two files of BPN-ISN.cif and BPN-ISN.ini in a single folder, and execute the following command to start the calculation. The structure and position of buthlparaben in the crystal are equivalent after and before the optimization.
C:\CONFLEX\bin\conflex-10a.exe -par C:\CONFLEX\par BPN-ISNenter
The command above is for Windows OS. For other OS, please refer to [How to execute CONFLEX].
[Output files]
After completing the calculation, you can obtain the output files listed below.
| File type | Explanation |
|---|---|
| (Input file name).bso | Detailed information on the crystal calculation is provided in this file. |
| (Input file name).ical | Powder X-ray diffraction data of the initial and optimized structures are provided in this file. |
| (Input file name)-F.cmf | The crystal structure data after optimization is provided in this file in CIFMIF file format (In the case of using cmf/mol file as input). |
| (Input file name)-F.cif | The rystal structure data after optimization is provided in this file in CIF file format (In the case of using cif file as input). |
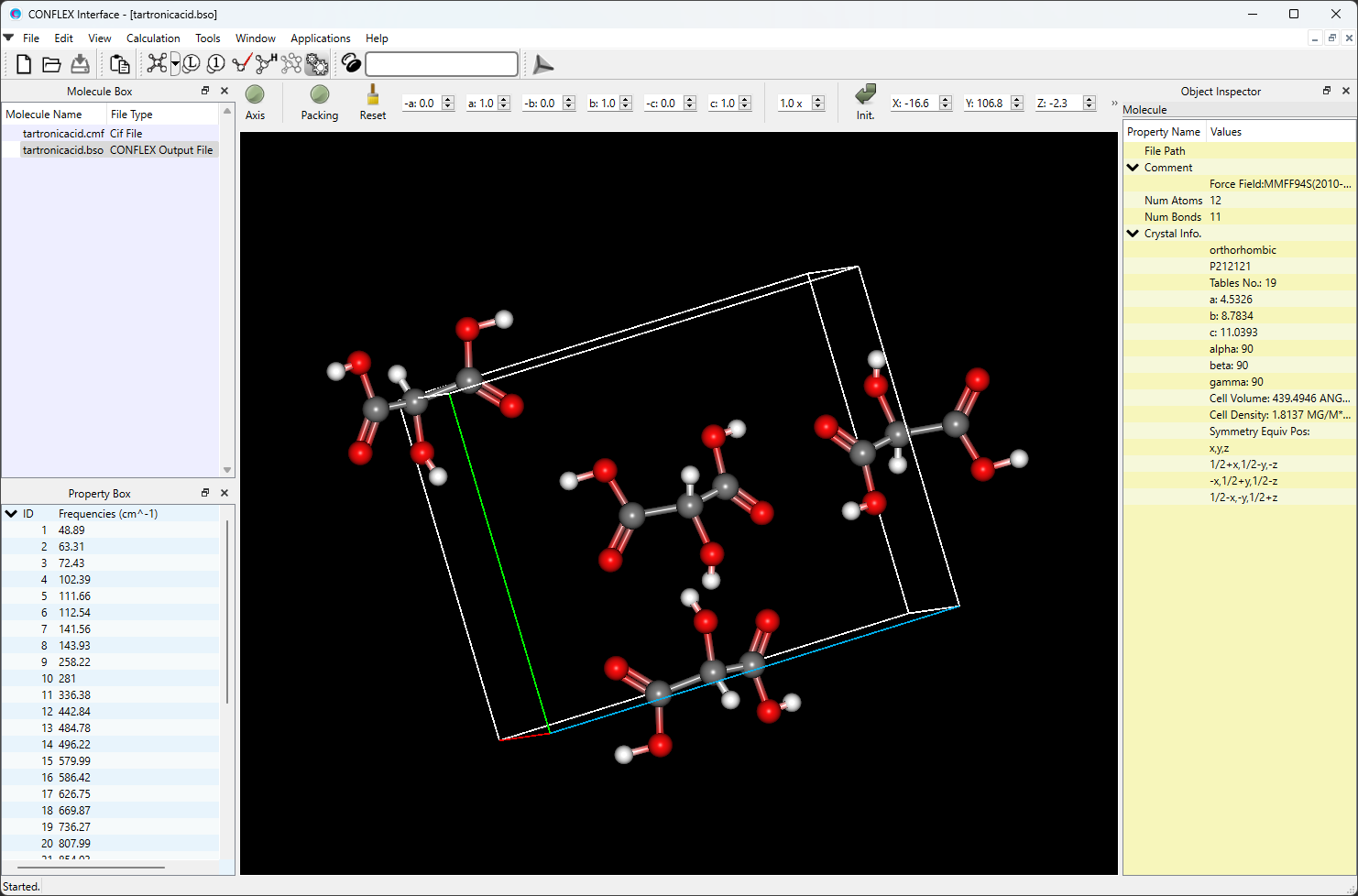
The [CRYSTAL STRUCTURE INFORMATION] section in the bso file provides information about the crystal structure model. In the bso file, these data are shown for both the initial and optimized structures. Below is the corresponding section from "tartronicacid.bso".
-------------------------- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE INFORMATION --------------------------
CRYSTAL SYSTEM: ORTHORHOMBIC
SPACE GROUP NAME: P212121
NUMBER: 19
SYMMETRY EQUIVALENT POSITION 1: x,y,z
2: 1/2+x,1/2-y,-z
3: -x,1/2+y,1/2-z
4: 1/2-x,-y,1/2+z
CELL LENGTHS a: 4.5326 ANGSTROM
b: 8.7834
c: 11.0393
CELL ANGLES alpha: 90.0000 DEGREE
beta: 90.0000
gamma: 90.0000
CELL VOLUME: 439.4946 ANGSTROM**3
CELL DENSITY: 1.8137 MG/M**3
Z : 4 (ZCFX: 4)
CRYSTAL RADIUS (VDW): 20.00 ANGSTROM
CRYSTAL RADIUS (COULOMBIC): 20.00 ANGSTROM
CRYSTAL PACKING GA: 15 (PGA: 8 NGA: -7)
GB: 11 (PGB: 6 NGB: -5)
GC: 9 (PGC: 5 NGC: -4)
NUM. OF ATOMS IN ASYMMETRIC UNIT: 12
NUM. OF MOLS IN ASYMMETRIC UNIT: 1
NUM. OF ATOMS IN UNIT CELL: 48
NUM. OF CALCULATED UNIT CELLS: 196
NUM. OF CALCULATED MOLECULES (VDW): 519
NUM. OF CALCULATED ATOMS (VDW): 6228
NUM. OF CALCULATED MOLECULES (COULOM.): 519
NUM. OF CALCULATED ATOMS (COULOM.): 6228
INTRAMOLECULAR ENERGY: 18.3350 KCAL/MOL
LATTICE ENERGY: -30.9465 KCAL/MOL
CRYSTAL ENERGY: -12.6115 KCAL/MOL
CALCULATED PRESSURE: -0.0000 GPa
ENTHALPY: -12.6115 KCAL/MOL
STRESS TENSOR (GPa): 1.11450E-13 0.0000 0.0000
0.0000 6.14966E-13 -1.72801E-20
0.0000 -1.72801E-20 -8.12269E-14
| Item | Explanation |
|---|---|
| CRYSTAL RADIUS(VDW): | Cutoff distance for vdW interactions |
| CRYSTAL RADIUS(COULOMBIC): | Cutoff distance for coulombic interactions on real space |
| CRYSTAL PACKING GA GB GC: | Packing area of the unit cell along a, b, and c axes |
| NUM. OF ATOMS IN ASYMMETRIC UNIT: | Total number of atoms in the asymmetric unit |
| NUM. OF MOLS IN ASYMMETRIC UNIT: | Total number of molecules in the asymmetric unit |
| NUM. OF ATOMS IN UNIT CELL: | Total number of atoms in the unit cell |
| NUM. OF CALCULATED UNIT CELLS: | Total number of unit cells in the crystal model |
| NUM. OF CALCULATED MOLECULES (VDW): | Total number of molecules included in the calculation of vdW interactions |
| NUM. OF CALCULATED ATOMS (VDW): | Total number of atoms included in the calculation of vdW interactions |
| NUM. OF CALCULATED MOLECULES (COULOM.) | Total number of molecules included in the calculation of coulombic interactions (real space) |
| NUM. OF CALCULATED ATOMS (COULOM.): | Total number of atoms included in the calculation of coulombic interactions (real space) |
| INTRAMOLECULAR ENERGY: | Eintra |
| LATTICE ENERGY: | Elattice |
| CRYSTAL ENERGY: | Ecrystal |
| CALCULATED PRESSURE: | Pressure calculated from the stress tensor |
| ENTHALPY: | Enthalpy |
| STRESS TENSOR (GPa): | Stress tensor |
The powder X-ray diffraction data of initial (NAME: INITIAL STRUCTURE) and optimized (NAME: FINAL STRUCTURE) structures are output to the ical file. Below is the corresponding section from "tartronicacid.ical".
------------ SIMULATED POWDER PATTERNS ------------
CID: 1
NAME: INITIAL STRUCTURE
X-RAY: Cu (KA1)
WAVE: 1.54059290
2*THETA: 0.000 - 50.000 , 0.020 STEP
H K L 2*THETA INTENSITY d
(DEGREE) (ANGSTROME)
0 0 0 0.000 0.000 0.00000
0 0 0 0.020 0.000 0.00000
0 0 0 0.040 0.000 0.00000
0 0 0 0.060 0.000 0.00000
0 0 0 0.080 0.000 0.00000
0 0 0 0.100 0.000 0.00000
* snip *
------------ SIMULATED POWDER PATTERNS ------------
CID: 2
NAME: FINAL STRUCTURE
X-RAY: Cu (KA1)
WAVE: 1.54059290
2*THETA: 0.000 - 50.000 , 0.020 STEP
H K L 2*THETA INTENSITY d
(DEGREE) (ANGSTROME)
0 0 0 0.000 0.000 0.00000
0 0 0 0.020 0.000 0.00000
0 0 0 0.040 0.000 0.00000
0 0 0 0.060 0.000 0.00000
0 0 0 0.080 0.000 0.00000
0 0 0 0.100 0.000 0.00000
* snip *
[Visualization of calculation results]
[If you executed the calculation using Interface]
After submitting a job, the Job Manager appears at the bottom of the CONFLEX interface window, displaying the status of the executed calculation. When the job status changes to "Finished", double-click the corresponding row (highlighted in red). The output file (.bso file) will open and the optimized structure will be displayed.
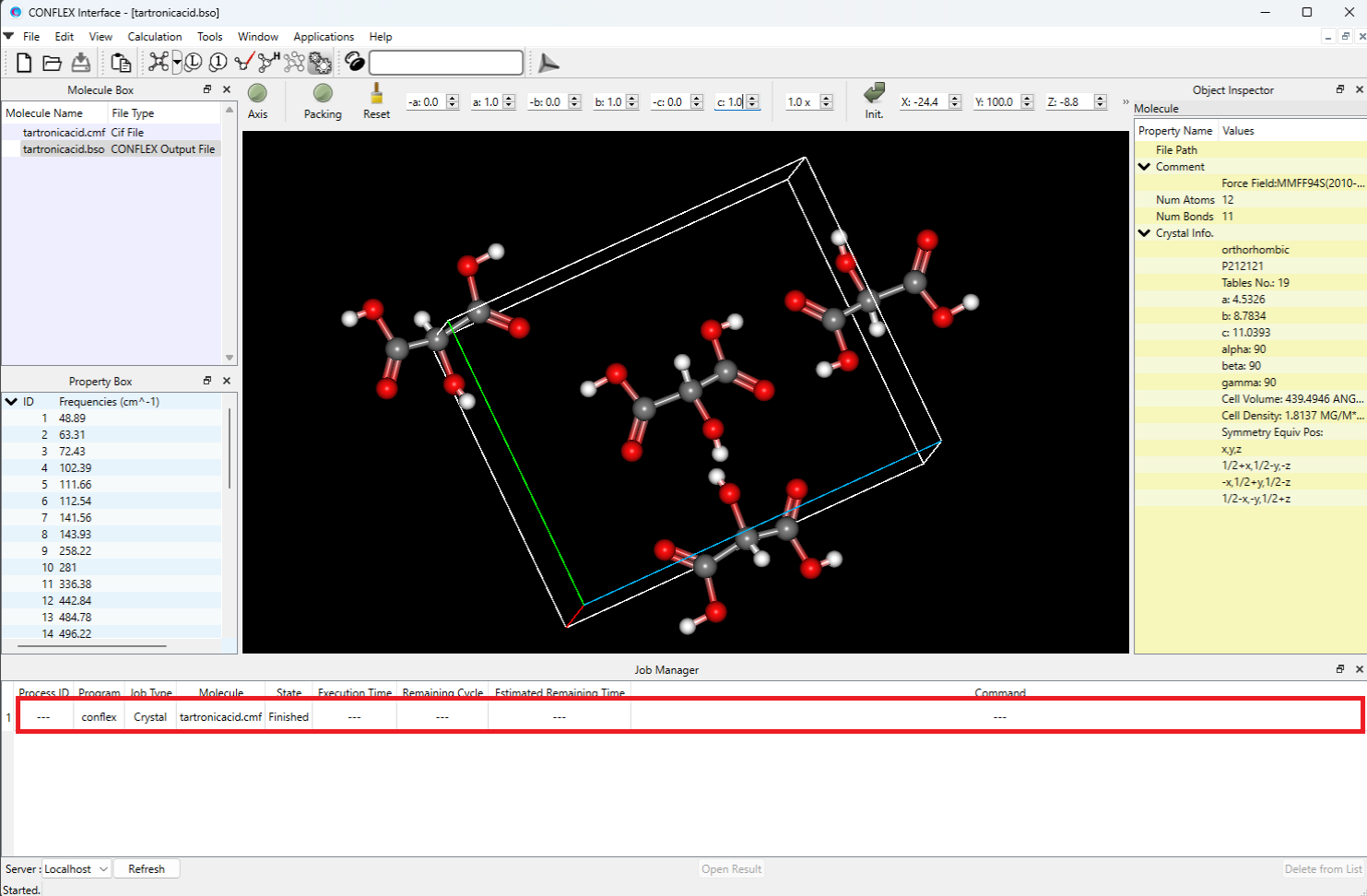
After opening the output file (-F.cmf or -F.cif file), you can display the powder X-ray diffraction pattern by selecting [Spectra_Analyzer] from [Application] menu.
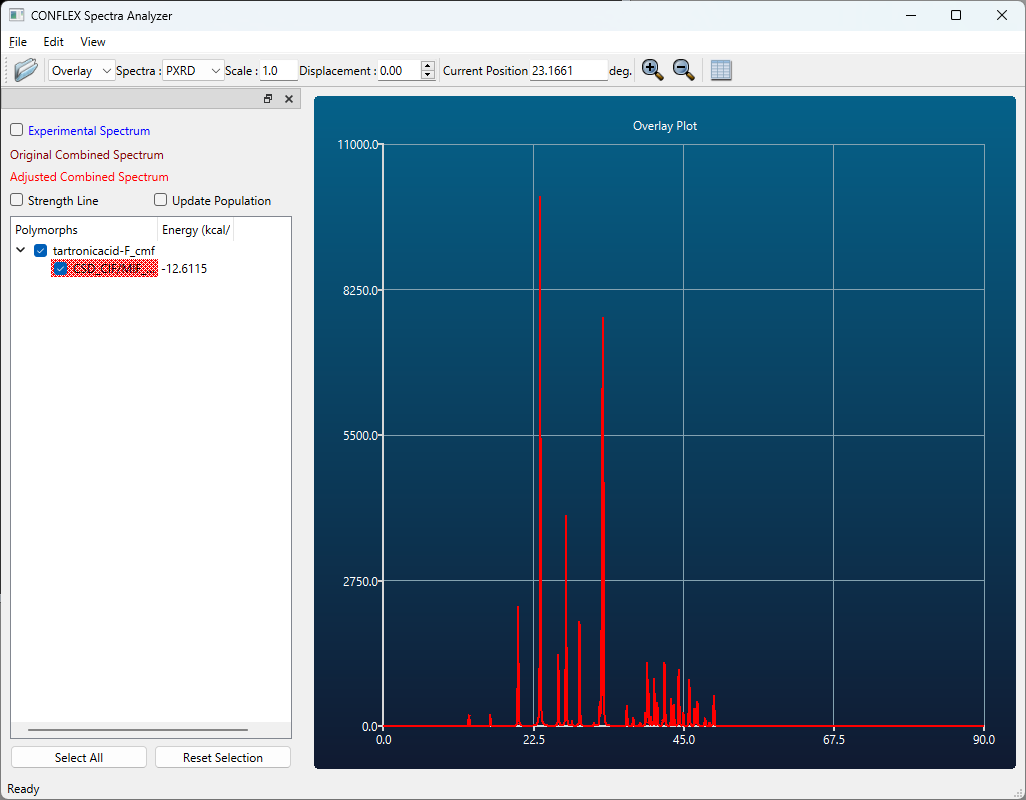
[If you executed the calculation using command line]
All output files will be stored in the folder containing the input files. By opeing the -F.cmf/-F.cif or .bso file, you can visualize the optimized crystal structure.
After opening the output file (-F.cmf or -F.cif file), you can display the powder X-ray diffraction pattern by selecting [Spectra_Analyzer] from [Application] menu.

[Available space groups]
| International Table Number | Space group name | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | P1 | |
| 2 | P-1 | |
| 3 | P2 | unique axis b |
| 3 | P2 | unique axis c |
| 4 | P21 | unique axis b |
| 4 | P21 | unique axis c |
| 5 | C2 | unique axis b |
| 5 | C2 | unique axis c |
| 6 | PM | unique axis b |
| 6 | PM | unique axis c |
| 7 | PC | unique axis b |
| 7 | PC | unique axis c |
| 8 | CM | unique axis b |
| 8 | CM | unique axis c |
| 9 | CC | unique axis b |
| 9 | CC | unique axis c |
| 10 | P2/M | unique axis b |
| 10 | P2/M | unique axis c |
| 11 | P21/M | unique axis b |
| 11 | P21/M | unique axis c |
| 12 | C2/M | unique axis b |
| 12 | C2/M | unique axis c |
| 13 | P2/C | unique axis b |
| 13 | P2/C | unique axis c |
| 14 | P21/C | unique axis b |
| 14 | P21/C | unique axis c |
| 15 | C2/C | unique axis b |
| 15 | C2/C | unique axis c |
| 16 | P222 | |
| 17 | P2221 | |
| 18 | P21212 | |
| 19 | P212121 | |
| 20 | C2221 | |
| 21 | C222 | |
| 22 | F222 | |
| 23 | I222 | |
| 24 | I212121 | |
| 25 | PMM2 | |
| 26 | PMC21 | |
| 27 | PCC2 | |
| 28 | PMA2 | |
| 29 | PCA21 | |
| 30 | PNC2 | |
| 31 | PMN21 | |
| 32 | PBA2 | |
| 33 | PNA21 | |
| 34 | PNN2 | |
| 35 | CMM2 | |
| 36 | CMC21 | |
| 37 | CCC2 | |
| 38 | AMM2 | |
| 39 | ABM2 | |
| 40 | AMA2 | |
| 41 | ABA2 | |
| 42 | FMM2 | |
| 43 | FDD2 | |
| 44 | IMM2 | |
| 45 | IBA2 | |
| 46 | IMA2 | |
| 47 | PMMM | |
| 48 | PNNN | origin choice 1 |
| 48 | PNNN | origin choice 2 |
| 49 | PCCM | |
| 50 | PBAN | origin choice 1 |
| 50 | PBAN | origin choice 2 |
| 51 | PMMA | |
| 52 | PNNA | |
| 53 | PMNA | |
| 54 | PCCA | |
| 55 | PBAM | |
| 56 | PCCN | |
| 57 | PBCM | |
| 58 | PNNM | |
| 59 | PMMN | origin choice 1 |
| 59 | PMMN | origin choice 2 |
| 60 | PBCN | |
| 61 | PBCA | |
| 62 | PNMA | |
| 63 | CMCM | |
| 64 | CMCA | |
| 65 | CMMM | |
| 66 | CCCM | |
| 67 | CMMA | |
| 68 | CCCA | origin choice 1 |
| 68 | CCCA | origin choice 2 |
| 69 | FMMM | |
| 70 | FDDD | origin choice 1 |
| 70 | FDDD | origin choice 2 |
| 71 | IMMM | |
| 72 | IBAM | |
| 73 | IBCA | |
| 74 | IMMA | |
| 75 | P4 | |
| 76 | P41 | |
| 77 | P42 | |
| 78 | P43 | |
| 79 | I4 | |
| 80 | I41 | |
| 81 | P-4 | |
| 82 | I-4 | |
| 83 | P4/M | |
| 84 | P42/M | |
| 85 | P4/N | origin choice 1 |
| 85 | P4/N | origin choice 2 |
| 86 | P42/N | origin choice 1 |
| 86 | P42/N | origin choice 2 |
| 87 | I4/M | |
| 88 | I41/A | origin choice 1 |
| 88 | I41/A | origin choice 2 |
| 89 | P422 | |
| 90 | P4212 | |
| 91 | P4122 | |
| 92 | P41212 | |
| 93 | P4222 | |
| 94 | P42212 | |
| 95 | P4322 | |
| 96 | P43212 | |
| 97 | I422 | |
| 98 | I4122 | |
| 99 | P4MM | |
| 100 | P4BM | |
| 101 | P42CM | |
| 102 | P42NM | |
| 103 | P4CC | |
| 104 | P4NC | |
| 105 | P42MC | |
| 106 | P42BC | |
| 107 | I4MM | |
| 108 | I4CM | |
| 109 | I41MD | |
| 110 | I41CD | |
| 111 | P-42M | |
| 112 | P-42C | |
| 113 | P-421M | |
| 114 | P-421C | |
| 115 | P-4M2 | |
| 116 | P-4C2 | |
| 117 | P-4B2 | |
| 118 | P-4N2 | |
| 119 | I-4M2 | |
| 120 | I-4C2 | |
| 121 | I-42M | |
| 122 | I-42D | |
| 123 | P4/MMM | |
| 124 | P4/MCC | |
| 125 | P4/NBM | origin choice 1 |
| 125 | P4/NBM | origin choice 2 |
| 126 | P4/NNC | origin choice 1 |
| 126 | P4/NNC | origin choice 2 |
| 127 | P4/MBM | |
| 128 | P4/MNC | |
| 129 | P4/NMM | origin choice 1 |
| 129 | P4/NMM | origin choice 2 |
| 130 | P4/NCC | origin choice 1 |
| 130 | P4/NCC | origin choice 2 |
| 131 | P42/MMC | |
| 132 | P42/MCM | |
| 133 | P42/NBC | origin choice 1 |
| 133 | P42/NBC | origin choice 2 |
| 134 | P42/NNM | origin choice 1 |
| 134 | P42/NNM | origin choice 2 |
| 135 | P42/MBC | |
| 136 | P42/MNM | |
| 137 | P42/NMC | origin choice 1 |
| 137 | P42/NMC | origin choice 2 |
| 138 | P42/NCM | origin choice 1 |
| 138 | P42/NCM | origin choice 2 |
| 139 | I4/MMM | |
| 140 | I4/MCM | |
| 141 | I41/AMD | origin choice 1 |
| 141 | I41/AMD | origin choice 2 |
| 142 | I41/ACD | origin choice 1 |
| 142 | I41/ACD | origin choice 2 |
| 143 | P3 | |
| 144 | P31 | |
| 145 | P32 | |
| 146 | R3 | hexagonal axes |
| 146 | R3 | rhombohedral axes |
| 147 | P-3 | |
| 148 | R-3 | hexagonal axes |
| 148 | R-3 | rhombohedral axes |
| 149 | P312 | |
| 150 | P321 | |
| 151 | P3112 | |
| 152 | P3121 | |
| 153 | P3212 | |
| 154 | P3221 | |
| 155 | R32 | hexagonal axes |
| 155 | R32 | rhombohedral axes |
| 156 | P3M1 | |
| 157 | P31M | |
| 158 | P3C1 | |
| 159 | P31C | |
| 160 | R3M | hexagonal axes |
| 160 | R3M | rhombohedral axes |
| 161 | R3C | hexagonal axes |
| 161 | R3C | rhombohedral axes |
| 162 | P-31M | |
| 163 | P-31C | |
| 164 | P-3M1 | |
| 165 | P-3C1 | |
| 166 | R-3M | hexagonal axes |
| 166 | R-3M | rhombohedral axes |
| 167 | R-3C | hexagonal axes |
| 167 | R-3C | rhombohedral axes |
| 168 | P6 | |
| 169 | P61 | |
| 170 | P65 | |
| 171 | P62 | |
| 172 | P64 | |
| 173 | P63 | |
| 174 | P-6 | |
| 175 | P6/M | |
| 176 | P63/M | |
| 177 | P622 | |
| 178 | P6122 | |
| 179 | P6522 | |
| 180 | P6222 | |
| 181 | P6422 | |
| 182 | P6322 | |
| 183 | P6MM | |
| 184 | P6CC | |
| 185 | P63CM | |
| 186 | P63MC | |
| 187 | P-6M2 | |
| 188 | P-6C2 | |
| 189 | P-62M | |
| 190 | P-62C | |
| 191 | P6/MMM | |
| 192 | P6/MCC | |
| 193 | P63/MCM | |
| 194 | P63/MMC | |
| 195 | P23 | |
| 196 | F23 | |
| 197 | I23 | |
| 198 | P213 | |
| 199 | I213 | |
| 200 | PM-3 | |
| 201 | PN-3 | origin choice 1 |
| 201 | PN-3 | origin choice 2 |
| 202 | FM-3 | |
| 203 | FD-3 | origin choice 1 |
| 203 | FD-3 | origin choice 2 |
| 204 | IM-3 | |
| 205 | PA-3 | |
| 206 | IA-3 | |
| 207 | P432 | |
| 208 | P4232 | |
| 209 | F432 | |
| 210 | F4132 | |
| 211 | I432 | |
| 212 | P4332 | |
| 213 | P4132 | |
| 214 | I4132 | |
| 215 | P-43M | |
| 216 | F-43M | |
| 217 | I-43M | |
| 218 | P-43N | |
| 219 | F-43C | |
| 220 | I-43D | |
| 221 | PM-3M | |
| 222 | PN-3N | origin choice 1 |
| 222 | PN-3N | origin choice 2 |
| 223 | PM-3N | |
| 224 | PN-3M | origin choice 1 |
| 224 | PN-3M | origin choice 2 |
| 225 | FM-3M | |
| 226 | FM-3C | |
| 227 | FD-3M | origin choice 1 |
| 227 | FD-3M | origin choice 2 |
| 228 | FD-3C | origin choice 1 |
| 228 | FD-3C | origin choice 2 |
| 229 | IM-3M | |
| 230 | IA-3D |
[Available X-ray sources]
| Kα1 wavelength (Ang.) | |
|---|---|
| Mg | 9.889554 |
| Al | 8.339514 |
| Si | 7.125588 |
| S | 5.3722 |
| Cl | 4.727818 |
| Ar | 4.191938 |
| K | 3.7412838 |
| Cr | 2.289726 |
| Mn | 2.101854 |
| Fe | 1.936041 |
| Co | 1.788996 |
| Ni | 1.65793 |
| Cu | 1.5405929 |
| Ga | 1.340127 |
| As | 1.175956 |
| Se | 1.10478 |
| Br | 1.039756 |
| Kr | 0.980267 |
| Zr | 0.7859579 |
| Mo | 0.70931715 |
| Ru | 0.6430994 |
| Rh | 0.6132937 |
| Pd | 0.5854639 |
| Ag | 0.55942178 |
| Cd | 0.5350147 |
| In | 0.5121251 |
| Sn | 0.4906115 |
| Sb | 0.47037 |
| Xe | 0.4163508 |
| Ba | 0.38512464 |
| Nd | 0.33185689 |
| Pm | 0.3201648 |
| Sm | 0.30904506 |
| Ho | 0.2607608 |
| Er | 0.25237359 |
| Tm | 0.24434486 |
| W | 0.20901314 |
| Au | 0.1801978 |
| Pb | 0.16537816 |
| Bi | 0.1607903 |