Calculation of water/octanol partition coefficient
[Calculation of log P value]
In molecular drug design, one of the important parameters for evaluating a designed molecule is the partition coefficient, log P. The log P is the common logarithm of the ratio P, which represents the concentration ratio of a solute between two solvents typically water and an organic solvent. It is widely used to assess the hydrophilicity or hydrophobicity of a solute.
The log P value can be calculated from the solvation free energies of the solute in water and in an organic solvent. CONFLEX can automatically calculate the water/octanol partition coefficient log Pow by calculating the solvation free energies in water and octanol using the GB/SA model. For details on calculating solvation free energy using the GB/SA model, please refer to [Calculation of solvation free energy].
[Relationship of log P value and solvation free energy]
The water/octanol partition coefficient log Pow is related to the solvation free energies (ΔGwat, ΔGoct) in water and octanol as follows:
where the R is gas constant, and the T is absolute temperature.
[Calculation of log P value]
This section explains how to calculate the log Pow of 1-butanol using it as an example.
Structure data of 1-Butanol (1-butanol.mol)
1-butanol.mol
15 14 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0999 V2000
-1.1802 -1.8691 -0.0000 C 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0.1388 -1.1076 -0.0000 C 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
-0.1388 0.3899 -0.0000 C 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1.1802 1.1514 -0.0000 C 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0.9247 2.5299 -0.0000 O 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
-0.9774 -2.9634 -0.0000 H 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
-1.7631 -1.6004 0.9093 H 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
-1.7637 -1.6001 -0.9088 H 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0.7217 -1.3763 -0.9093 H 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0.7223 -1.3766 0.9088 H 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
-0.7217 0.6586 0.9093 H 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
-0.7223 0.6589 -0.9088 H 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1.7631 0.8827 -0.9093 H 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1.7637 0.8824 0.9088 H 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1.7610 2.9634 -0.0000 H 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 2 1 0
1 6 1 0
1 7 1 0
1 8 1 0
2 3 1 0
2 9 1 0
2 10 1 0
3 4 1 0
3 11 1 0
3 12 1 0
4 5 1 0
4 13 1 0
4 14 1 0
5 15 1 0
M END
[Execution from Interface]
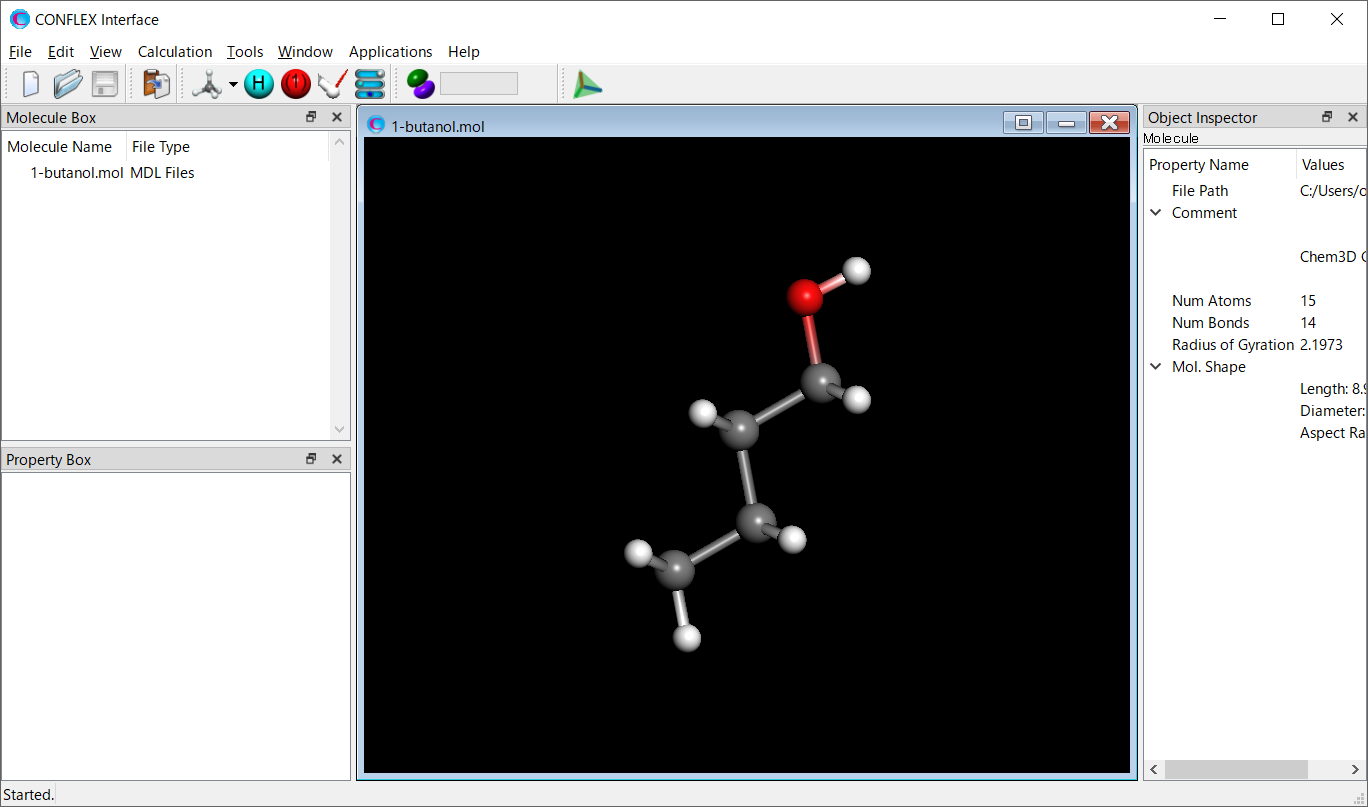
Open the 1-butanol.mol file using CONFLEX Interface.
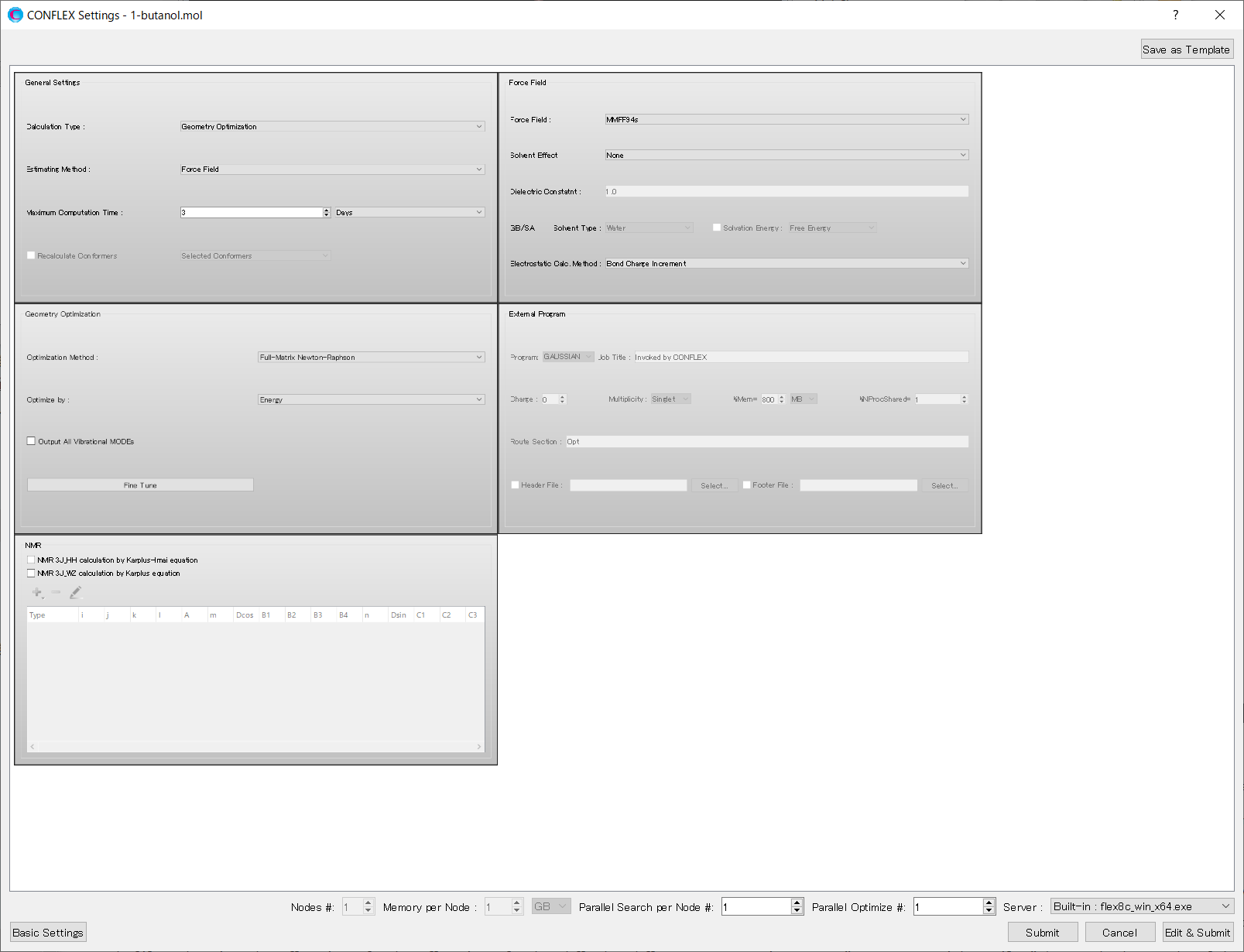
Select [CONFLEX] from the Calculation menu, and then click in the calculation setting dialog that appears. A detailed settings dialog will be displayed.
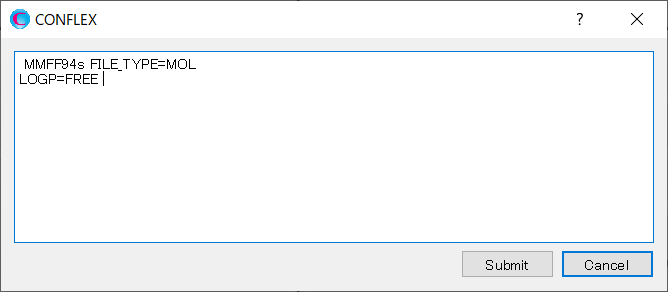
Click at the bottom right of the Detailed Settings dialog, and add [LOGP=FREE] in the dialog that appears. By adding this keyword, the log Pow will be calculated based on solvation free energies obtained through vibrational analyses in water and octanol.
After completing the calculation settings, click to start the calculation.
The [LOGP=] keyword has three options: [FREE], [OPTIMZ], and [SINGLE]. By selecting one of these options, you can choose the level of approximation used to calculate the solvation free energies. For details on how each option corresponds to a specific approximation level, please refer to [Calculation of solvation free energy].
[Execution from command line]
The calculation settings are defined by specifying keywords in the 1-butanol.ini file.
1-butanol.ini file
MMFF94S LOGP=FREE
[LOGP=FREE] means that log Pow is calculated using solvation free energies obtained from vibrational analyses in both water and octanol solvents
[MMFF94S] means that MMFF94s force field is used.
The [LOGP=] keyword has three options: [FREE], [OPTIMZ], and [SINGLE]. By selecting one of these options, you can choose the level of approximation used to calculate the solvation free energies. For details on how each option corresponds to a specific approximation level, please refer to [Calculation of solvation free energy].
Store the 1-butanol.mol and 1-butanol.ini files in a single folder, and execute the following command to start the calculation.
C:\CONFLEX\bin\conflex-10a.exe -par C:\CONFLEX\par 1-butanolenter
The command above is for Windows OS. For other OS, please refer to [How to execute CONFLEX].
Calculation results
The results of the log Pow calculation for 1-butanol are shown below (1-butanol.bso). The calculations are performed in the following order: gas phase, octanol solvent, and water. After the calculations in octanol and water are completed, the corresponding solvation free energies will be displayed.
Solvation free energy of 1-Butanol in octanol
SOLVATION ENERGY (DIFF. OF TOTAL ENERGY) = -5.85364 (KCAL/MOL) SOLVATION ENERGY (DIFF. OF FREE ENERGY) = -5.92111 (KCAL/MOL)
Solvation free energy of 1-Butanol in water
SOLVATION ENERGY (DIFF. OF TOTAL ENERGY) IN WATER = -4.50971 (KCAL/MOL) SOLVATION ENERGY (DIFF. OF FREE ENERGY) IN WATER = -4.72882 (KCAL/MOL)
When all calculations are finished, the log Pow value (0.875), calculated from the solvation free energies, is output at the end of the bso file. The experimental log Pow value is 0.88.
Summary of the log Pow calculation (1-butanol.bso file)
!------------------------------------------------------------------------------------! ! ! ! *** SUMMARY OF LOGP CALCULATION *** ! ! ! ! FORMULA: LOGP = (DELTAG(WATER) - DELTAG(OCTANOL))/(2.30*R*T) ! ! (R = 1.9872065 (CAL/(K*MOL)) T = 298.15 (KELVIN)) ! ! ! ! DELTAG(WATER) = -4.72882 (KCAL/MOL) ! ! DELTAG(OCTANOL) = -5.92111 (KCAL/MOL) ! ! ! ! LOGP = 0.875 ! ! ! !------------------------------------------------------------------------------------!